How Big is the Sun?
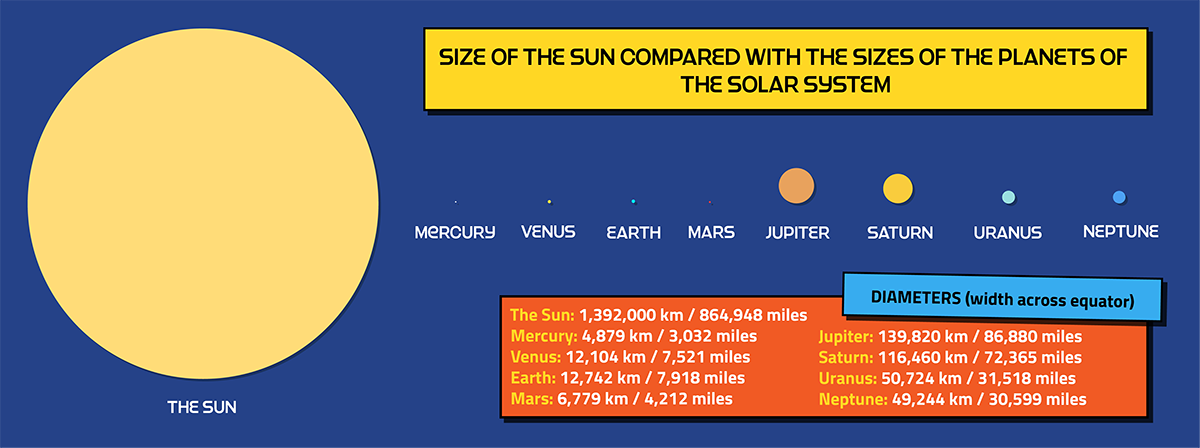
The Sun is huge! It is the largest object in the Solar System with a diameter of about 1,392,000 kilometres (864,948 miles). It is so large that every single other known item in the Solar System would be able to fit inside of it. This includes all of the planets, dwarf planets, moons, comets, asteroids, meteroids and any other bits of rock that happen to be floating around. To get an idea of how large it actually is, let's compare it to some other objects.
If the Sun were the size of a basketball...
Earth would be about as wide as a grain of rice. Earth is so tiny in comparison that 1.3 million Earths could be squeezed into the Sun. Remember, Earth is a planet large enough to be home to you and 7 billion other people, but is nothing more than a dot in space. A very special dot though!
Scientists like to group stars into categories with other similar stars. The Sun is classified as a yellow dwarf star. Although it is clearly gigantic when compared to everything else in the Solar System, it is actually fairly small when measured against some other stars. For example, Betelguese is a red supergiant which is about 700 times wider than the Sun. If Betelguese existed in the Solar System, it would stretch out so far that it would engulf all of the Inner Planets.

The Sun is big, but it's going to get even bigger!
The Sun hasn't been around forever, nor will it last forever. Instead, the Sun, like all stars, was born and will eventually die. A star's life is very very long, so you're not going to wake up any time soon and find that the Sun has vanished! The Sun should have a life of about 10 billion years and is roughly half way through its life. It will remain in its current yellow dwarf state for quite some time.
The Sun is mostly made up of a gas called hydrogen. It generates its heat and light by turning its hydrogen into helium through a process called nuclear fusion. This is an exposive process which takes place at the Sun's core. The energy generated from explosions travels outwards until it reaches the Sun's visible surface and causes it to be hot and bright.
Nuclear fusion is a continuous process but eventually, in about 4 to 5 billion years, the Sun will run out of its supply of hydrogen. As it continues to burn off its remaining gases, it will begin to cool and shine more dimly. It will also expand in size and will become a red giant. It could possibly grow large enough to consume some of the Inner Planets, maybe even Earth. It'll stay like that for about a billion years, until it rapidly shrinks down to become a white dwarf star, perhaps no larger than Earth and not shining brightly at all. Its outer layers will gently shed away from it and form a gassy cloud, known as a planetary nebula. The cloud will remain luminated by any remaining heat held within the gases and from the weak light of the Sun. After a few thousand years, the gases will disperse into space and the remaining light of the white dwarf star will go out. The Sun will be nothing more than a black dwarf, and its Solar System will be no more.
Well, that's a cheery end to this page!